https://www.techworld-with-nana.com/devops-bootcamp
What Is Docker?
Docker is an open-source containerization platform that allows developers to package applications — along with all their dependencies and configurations — into portable, standardized containers.
Containers existed before Docker, but Docker made them accessible, consistent, and developer-friendly.
Why It Matters
- Same app, same behavior across environments
- Fast installation and deployment
- Easier version management
- Eliminates “it works on my machine” issues
What Is a Container?
A container is a lightweight, isolated environment for an application and its dependencies. It’s portable across machines and ideal for efficient development, shipment, and deployment.
Before Docker:
Manual setup, dependency conflicts, inconsistent environments.
After Docker:
Self-contained packages, predictable runtime, reproducible builds.
Docker Images vs Containers
| Docker Image | Docker Container |
|---|---|
| Blueprint of an app | Running instance of that blueprint |
| Static, layered artifact | Active environment executing the app |
| Can be shared, versioned, and stored | Exists while running (ephemeral unless persisted) |
Containers vs Virtual Machines
| Containers | Virtual Machines |
|---|---|
| Share the host OS kernel | Each VM includes a full OS |
| Faster startup | Slower startup |
| Lightweight | Heavy |
| App-level isolation | Hardware-level isolation |
Docker Architecture
Docker consists of:
- Client (CLI): Interface to run Docker commands
- Server (Daemon): Executes build/run tasks
- Registry: Stores and distributes images
It also manages:
- Images and containers
- Networking between containers
- Data persistence via volumes
Essential Docker Commands
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
docker run |
Create and start a container |
docker pull |
Download an image |
docker ps / docker ps -a |
List running/all containers |
docker images |
List local images |
docker logs <container> |
View container logs |
docker exec -it <container> bash |
Open a terminal inside a running container |
docker stop/start |
Manage container lifecycle |
Ports in Docker
Since multiple containers can run simultaneously, Docker uses port mapping:
docker run -p 8080:80 my-app- Host port: 8080
- Container port: 80
Now your app is accessible at localhost:8080.
Workflow With Docker
- Build image from a
Dockerfile - Run container from that image
- Map ports and mount volumes as needed
- Push/pull images from repositories
- Deploy containers to remote servers
Docker Compose
Docker Compose helps manage multi-container applications with a single YAML file.
Example:
version: '3'
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "8080:80"
db:
image: mongo:4.2Benefits:
- Shared network automatically created
- Centralized configuration
- Easier updates and orchestration
Dockerfile Basics
A Dockerfile defines how to build an image:
FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN npm install
CMD ["npm", "start"]Common Instructions
FROM– Base imageCOPY/ADD– Add filesRUN– Execute build commandsEXPOSE– Declare portsCMD/ENTRYPOINT– Start the app
Each instruction creates a new layer, making builds efficient through caching.
Private & Public Repositories
Public: DockerHub
Private: AWS ECR, Azure Container Registry, Nexus, etc.
To push to a private registry:
docker login <registry-url>
docker tag my-app:1.0 <registry-url>/my-app:1.0
docker push <registry-url>/my-app:1.0Docker Volumes
By default, container data disappears when the container is removed. Volumes solve this by persisting data outside the container.
Types of Volumes
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Host Volume | Maps a specific host directory |
| Anonymous Volume | Created automatically (not referenced by name) |
| Named Volume | Managed by Docker, referenced by name |
Example:
docker run -v mydata:/var/lib/mysql/data mysqlOr inside docker-compose.yaml:
volumes:
dbdata:
services:
db:
image: mongo
volumes:
- dbdata:/data/dbDocker Best Practices
Security
- Use official images
- Avoid leaking credentials into images
- Run as non-root users
- Regularly scan for vulnerabilities
Efficiency
- Use minimal base images (e.g., Alpine)
- Cache layers intelligently
- Add a
.dockerignore - Use multi-stage builds for smaller, cleaner images
Demo Projects
Use Docker for Local Development
Final Project Code: https://github.com/xwindwolf/twn-devops-m7-docker
Technologies Used
- Docker
- Node.js
- MongoDB
- MongoExpress
Summary of Steps
- Create Dockerfile for Nodejs application and build Docker image.
- Run Nodejs application in Docker container and connect to MongoDB database container locally.
- Also run MongoExpress container as a UI of the MongoDB database.
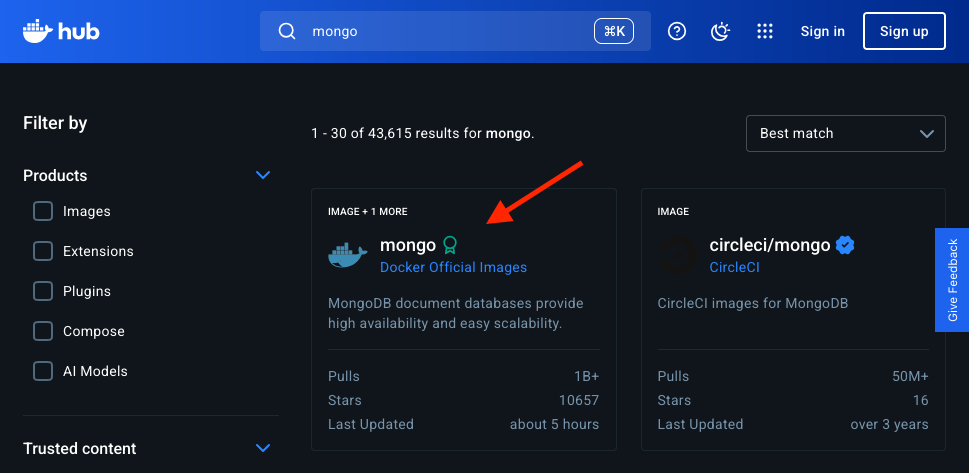
Search and Pull Docker Images
Most of the public images are available through https://hub.docker.com/.
- Go to https://hub.docker.com/
- Search for
mongoimage.
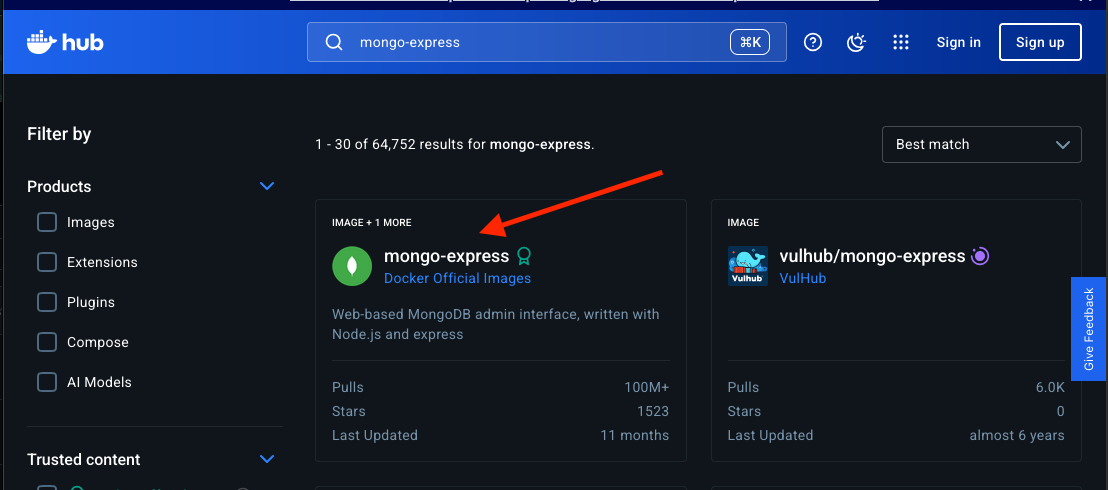
- Search for
mongo-expressimage.
- Pull the
latestimage for each.
docker pull mongo
docker pull mongo-express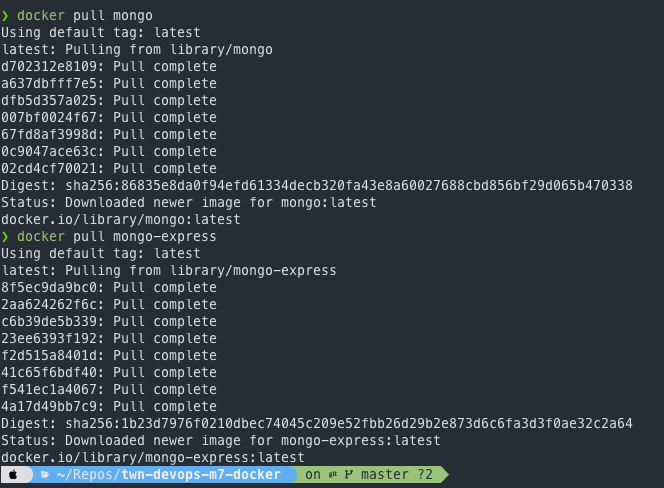
Run Mongo and Mongo-Express Docker Images
Docker Compose - Running Multiple Services
Technologies Used
- Docker
- MongoDB
- MongoExpress
Summary of Steps
- Write Docker Compose file to run MongoDB and MongoExpress containers.
Dockerize Nodejs Application
Technologies Used
- Docker
- Node.js
Summary of Steps
- Write Dockerfile to build a Docker image for a Nodejs application.
Persist Data with Docker Volumes
Technologies Used
- Docker
- Node.js
- MongoDB
Summary of Steps
- Persist data of a MongoDB container by attaching a Docker volume to it.
Create Docker Repository on Nexus and Push to It
Technologies Used
- Docker
- Nexus
- DigitalOcean
- Linux
Summary of Steps
- Create Docker hosted repository on Nexus.
- Create Docker repository role on Nexus.
- Configure Nexus, DigitalOcean Droplet and Docker to be able to push to Docker repository.
- Build and Push Docker image to Docker repository on Nexus.
Deploy Docker Application on a Server with Docker Compose
Technologies Used
- Docker
- AmazonECR
- Node.js
- MongoDB
- MongoExpress
Summary of Steps
- Copy Docker-Compose file to remote server.
- Login to private Docker registry on remote server to fetch our app image.
- Start our application container with MongoDB and MongoExpress services using docker compose.
Deploy Nexus as Docker Container
Technologies Used
- Docker
- Nexus
- DigitalOcean
- Linux
Summary of Steps
- Create and Configure Droplet.
- Set up and run Nexus as a Docker container.
